What Are The Different Vent Circuit Types?
Ventilation circuits play a crucial role in the provision of respiratory support to patients requiring mechanical ventilation. Understanding the different types of vent circuits is essential for healthcare professionals involved in critical care settings. This article provides an in-depth exploration of various vent circuits, including passive and active systems, as well as specialized modes such as High Frequency Oscillation Ventilation (HFOV), Pressure Control Ventilation (PCV), and Volume Control Ventilation (VCV). By delving into the nuances of each circuit type and their applications, readers will gain valuable insights into selecting the most appropriate ventilation strategy for individual patient needs.
Introduction to Vent Circuits
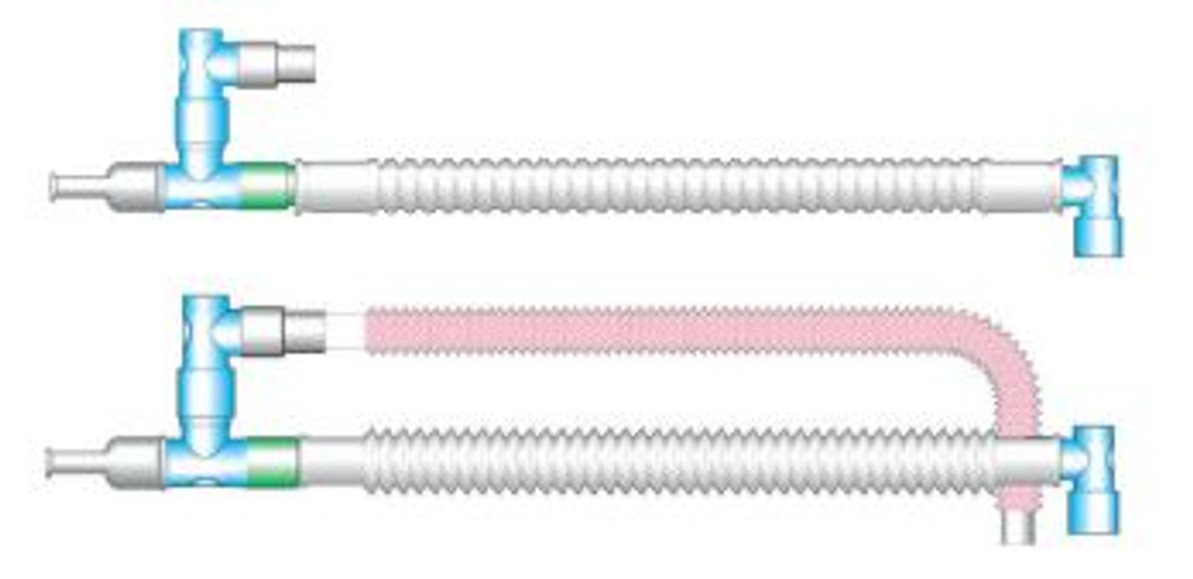
Vent circuits are essential components in mechanical ventilation systems that help deliver oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the lungs. These circuits play a crucial role in assisting patients with breathing difficulties and maintaining adequate oxygen levels in their bodies.
Passive Vent Circuits
Characteristics of Passive Vent Circuits
Passive vent circuits rely on the patient's own respiratory efforts to draw in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. They do not require any external power source to function, making them simple and cost-effective solutions for ventilation support.
Types of Passive Vent Circuits
There are different types of passive vent circuits, including simple non-rebreathing circuits and reservoir bags that help deliver higher concentrations of oxygen to patients. These circuits are useful in situations where the patient can breathe independently but may benefit from additional oxygen support.
Active Vent Circuits
Key Features of Active Vent Circuits
Active vent circuits utilize mechanical components such as ventilators to assist or control the patient's breathing. These circuits provide more precise control over ventilation settings and can adjust parameters like tidal volume and respiratory rate based on the patient's needs.
Advantages and Considerations for Active Vent Circuits
Active vent circuits offer advantages such as increased control over ventilation parameters, better synchronization with the patient's breathing patterns, and the ability to provide different modes of ventilation. However, they may require more complex monitoring and maintenance compared to passive circuits.
High Frequency Oscillation Ventilation (HFOV)
Principles of HFOV
HFOV is a specialized form of mechanical ventilation that delivers very small, rapid breaths at a high frequency to improve gas exchange in the lungs. This technique helps maintain lung recruitment and can be beneficial for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or other severe lung conditions.
Applications and Benefits of HFOV
HFOV can provide better oxygenation and ventilation for patients with challenging respiratory conditions. It is particularly useful in cases where conventional ventilation methods may be ineffective or harmful. However, HFOV requires specialized equipment and trained healthcare professionals for safe and effective implementation.
Pressure Control Ventilation (PCV)
Working Mechanism of PCV
In Pressure Control Ventilation (PCV), the ventilator delivers breaths at a set pressure level. This means that the ventilator maintains a constant pressure during the inspiratory phase, allowing for better control over the tidal volume delivered to the patient.
Indications for PCV Use
PCV is often used in patients with conditions such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), where minimizing barotrauma and volutrauma is crucial. It can also be beneficial in patients with dynamic hyperinflation or those who require lower tidal volumes to reduce lung injury.
Volume Control Ventilation (VCV)
Understanding VCV Mode
Volume Control Ventilation (VCV) delivers a preset tidal volume to the patient with each breath. The ventilator adjusts the pressure needed to deliver the set volume, making it a reliable option for maintaining consistent ventilation.
Comparison with Other Ventilation Modes
Compared to pressure control ventilation, VCV provides a more predictable tidal volume delivery. It is commonly used in patients with normal lung compliance or those requiring precise control over tidal volume delivery.
Dual Control Ventilation
Explanation of Dual Control Mode
Dual Control Ventilation combines aspects of both pressure control and volume control modes. This mode allows clinicians to set both pressure and volume targets, providing more flexibility in managing ventilation parameters.
Clinical Applications and Effectiveness
Dual Control Ventilation is advantageous in patients with complex respiratory conditions or variable lung compliance. It offers clinicians the ability to tailor ventilation settings to individual patient needs, improving overall ventilation efficacy.
Considerations for Selecting Vent Circuits
Factors to Consider in Vent Circuit Selection
When selecting vent circuits, factors such as patient's lung mechanics, ventilator capabilities, and clinical goals should be taken into account. Choosing the appropriate circuit can significantly impact ventilation outcomes.
Patient-Specific Considerations
Patient-specific considerations, including lung pathology, airway resistance, and ventilatory requirements, play a critical role in vent circuit selection. Tailoring the circuit setup to meet the unique needs of each patient can optimize ventilation and enhance patient outcomes.In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the different types of ventilation circuits is imperative for optimizing patient care and outcomes in critical care settings. By familiarizing oneself with the characteristics and applications of passive and active vent circuits, as well as specialized modes like HFOV, PCV, and VCV, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable ventilation strategy for each patient. Through continued education and awareness of evolving technologies in respiratory support, healthcare providers can enhance their ability to deliver effective and personalized care to those in need of mechanical ventilation.
Recent Posts
-
Dual -Limb vs. Single-Limb Vent Circuits - What Is The Difference?
When it comes to different vent circuit types, there are a few key distinctions to be aware of. The …Dec 17th 2024 -
What Are The Different Vent Circuit Types?
Ventilation circuits play a crucial role in the provision of respiratory support to patients requiri …Nov 4th 2024 -
What is Medical oxygen commonly used for?
Medical Oxygen (gaseous) is used whenever you are not getting enough oxygen into your blood. This si …Jan 24th 2023